|
|
Collection of ThingsStudents will create four compositions with one thematic subject. The compositions will emulate four different artistic styles of famous artists from different artistic movements.
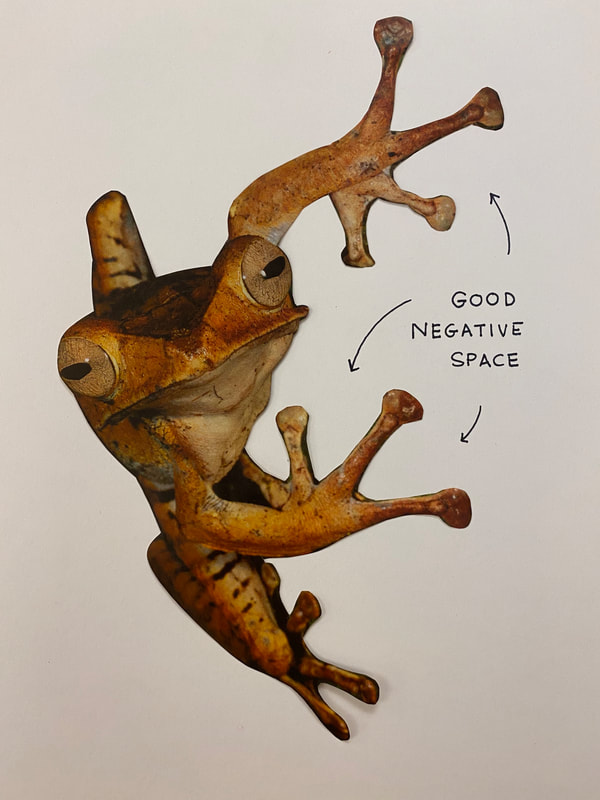
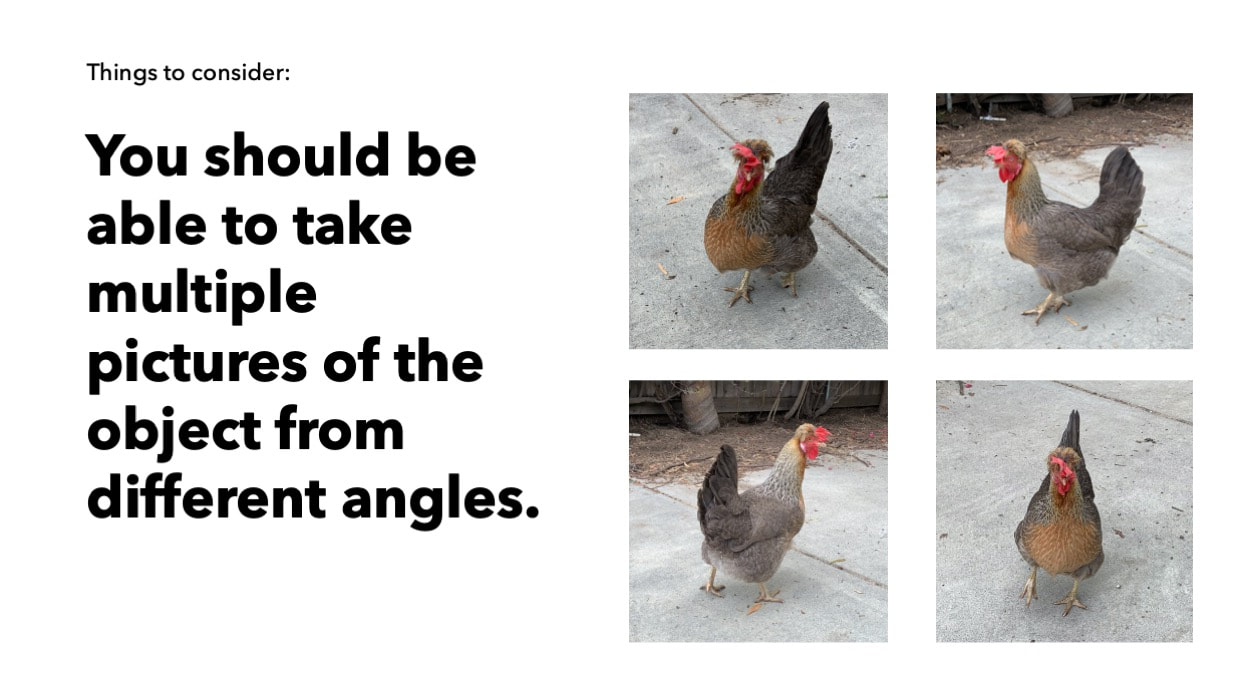
Students will use reference images for their compositional subject and think through compositional concerns, such as cropping, color palette, light and shadow, depth and flatness, negative space, and eye movement. |
Materials
|
Content
|
|
Project Overview
|
CHOOSE AN OBJECT TO BE THE SUBJECT OF FOUR COMPOSITIONS
LEARN ABOUT DIFFERENT ART STYLES
CHOOSE FOUR ART STYLES
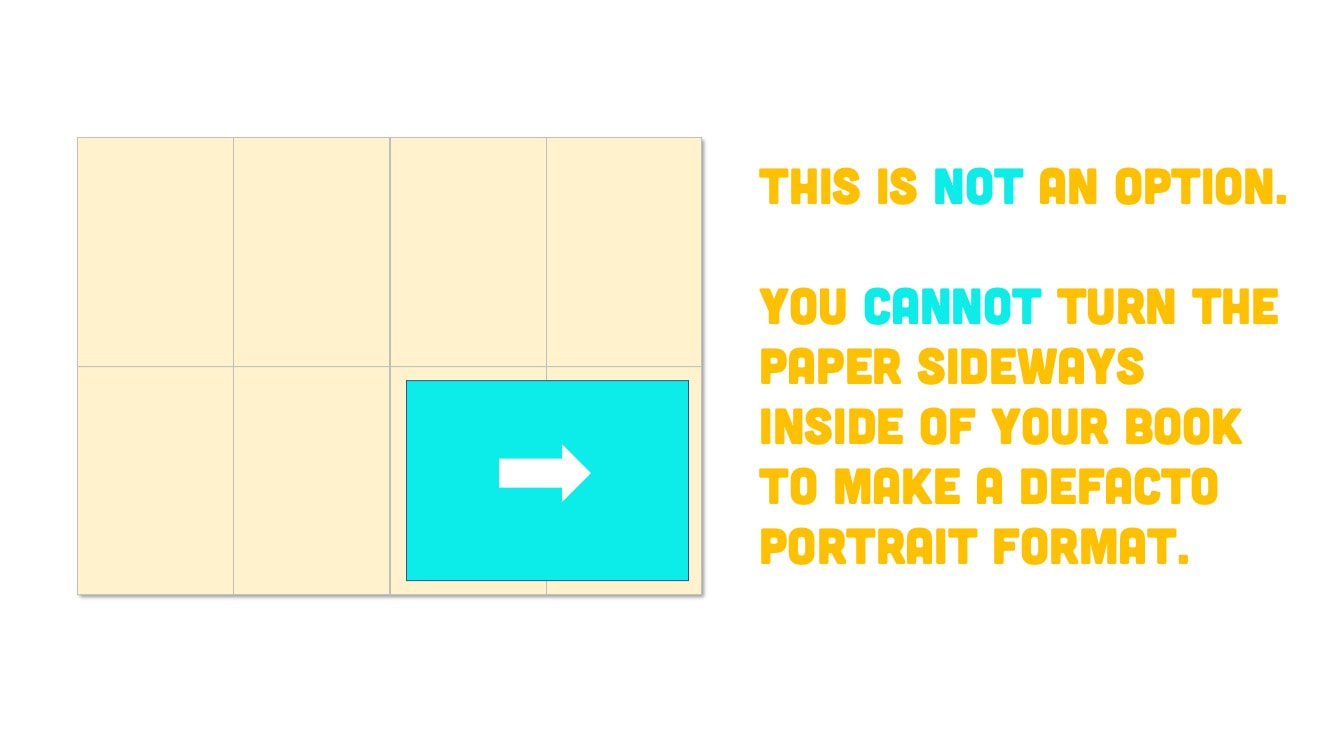
COMPOSITION FORMAT
|
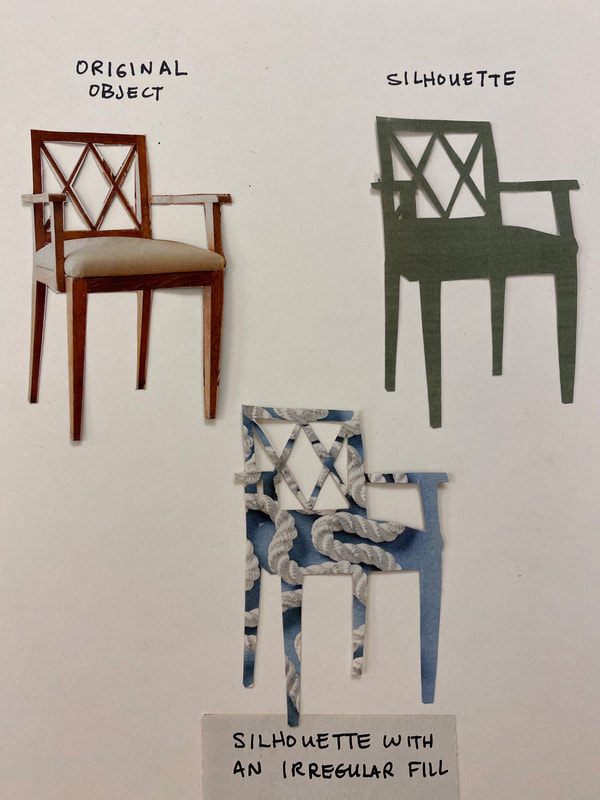
Choosing the Subject of Your Compositions
|
IT'S A GREAT IDEA TO CHOOSE SOMETHING RECOGNIZABLE, RATHER THAN SOMETHING REALLY OBSCURE.
The more obscure the subject is, the higher skill level you'll need to pull it off. The more recognizable the subject is, the more forgiving your art talents can be because people will understand what it is with less visual information. |
CHOOSE AN OBJECT TO BE THE SUBJECT OF FOUR COMPOSITIONS
INTERESTING SILHOUETTE
|
Reference Images for Your Subject
OPTION 1 : PHOTOS FROM THE INTERNET
OPTION 2 : PHOTOS YOU TAKE AT HOME
Researching Art Styles
|
CHOOSE AN ART STYLE TO LEARN ABOUT
PAY ATTENTION TO THE PLACE AND TIME FOR THE ART STYLE
USING ART MUSEUM SOURCES IS BETTER THAN A GOOGLE SEARCH
Places to StartYou can look up your own preferred art styles and movements on your own, or choose from some of the art styles listed below.
When looking for style reference artwork, be sure to choose works from the time in history the style originated in. You don't want to accidentally get contemporary copies of past styles as your reference examples. Use museum galleries rather than google search to find the artwork. |
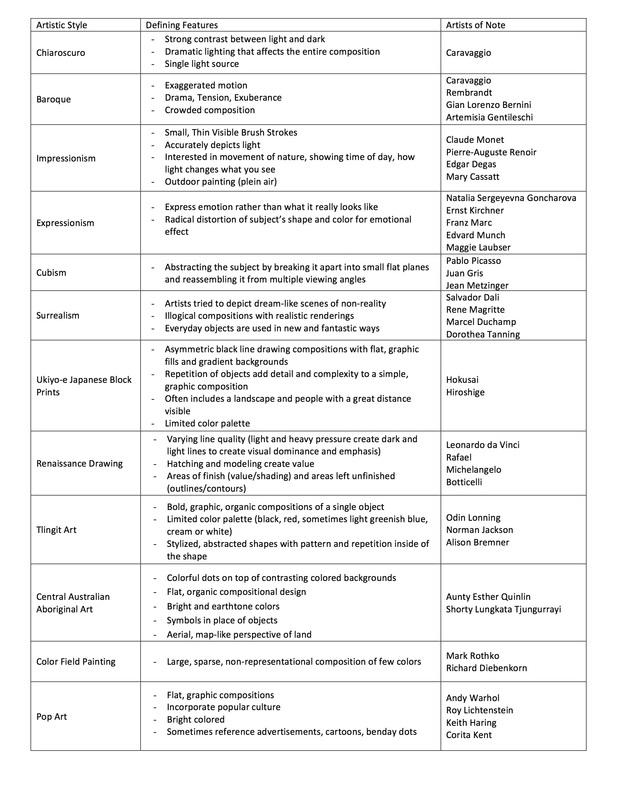
Art Styles & Movements
|
GENERAL ART HISTORY OVERVIEW
VIDEO: A Timeline of Visual Art Movements |
|
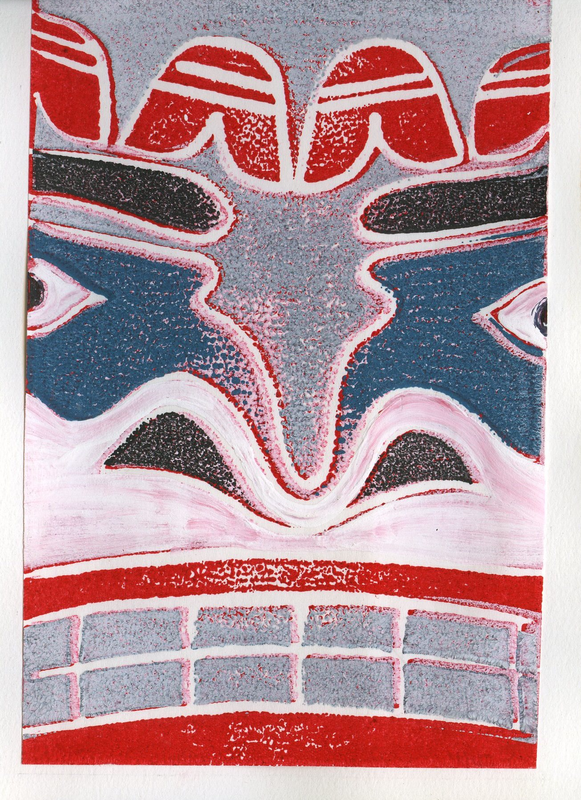
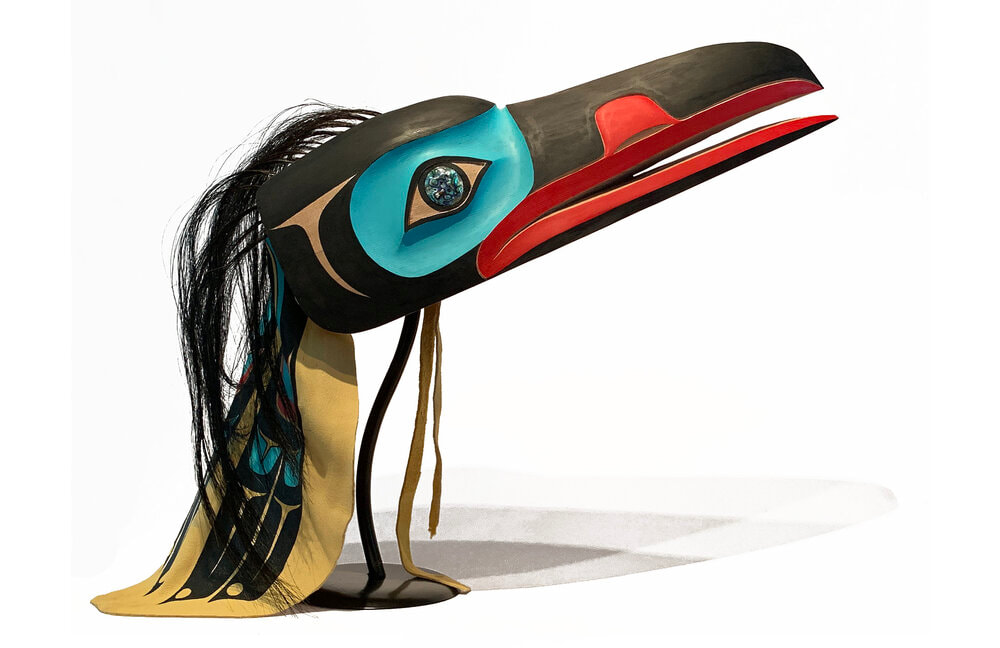
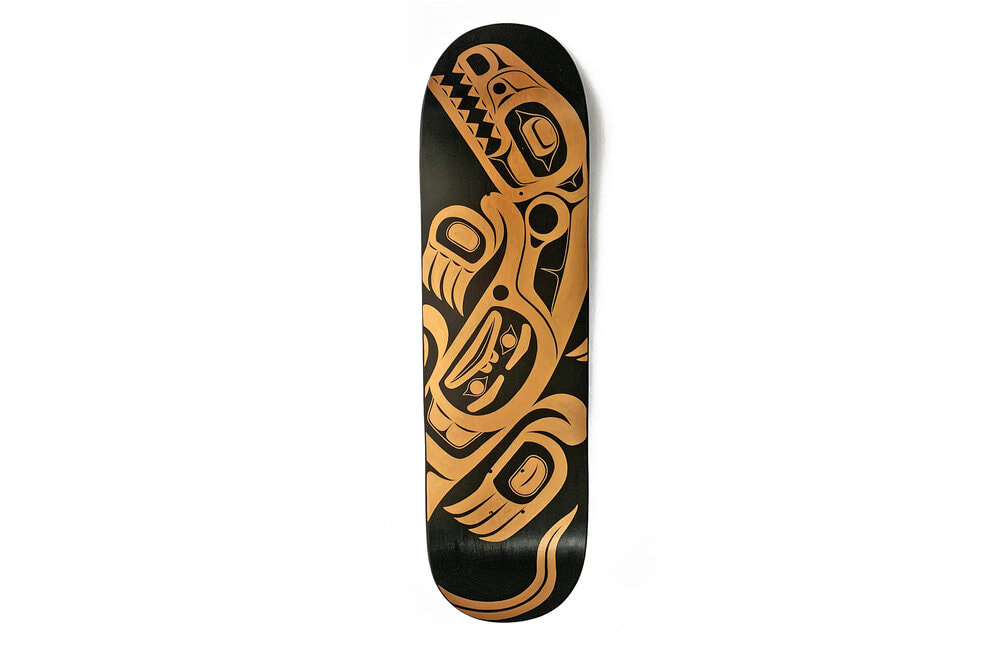
TLINGIT ART
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 9000 BCE - PRESENT DAY (Entrance into the western art market in 1800) Indigenous Peoples of Alaska and Northern Canada DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Contemporary Tlingit Painting |
|
ANCIENT EGYPTIAN ART
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION : 3100 BCE - 300 CE EGYPT DEFINING FEATURES:
|
|
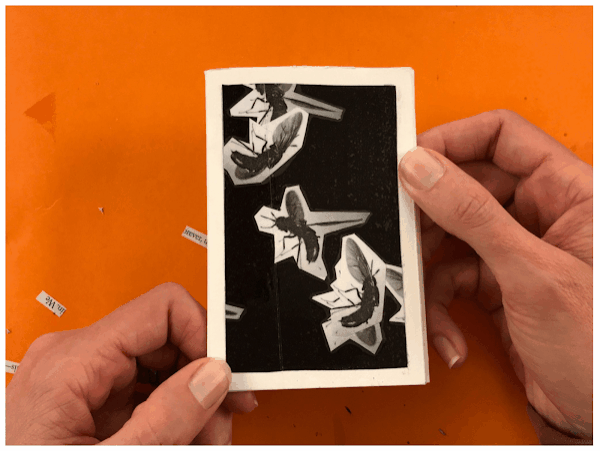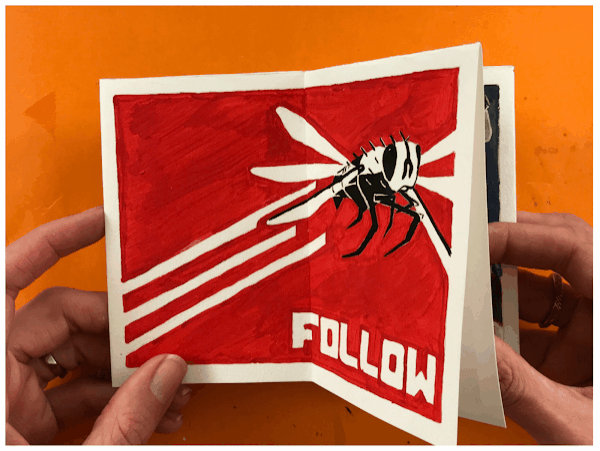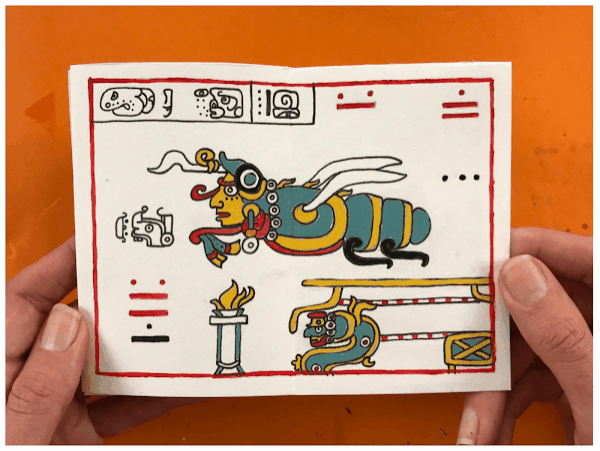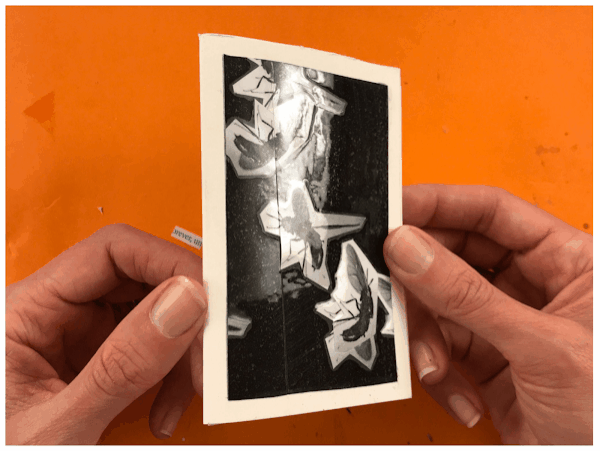
ANCIENT MAYAN
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 400 - 1400 CENTRAL AMERICA DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Maya Blue - LittleArtTalks MAYAN CODEX |
|
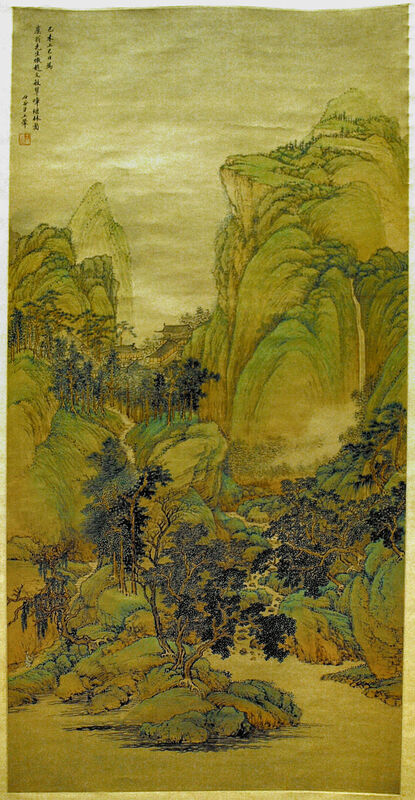
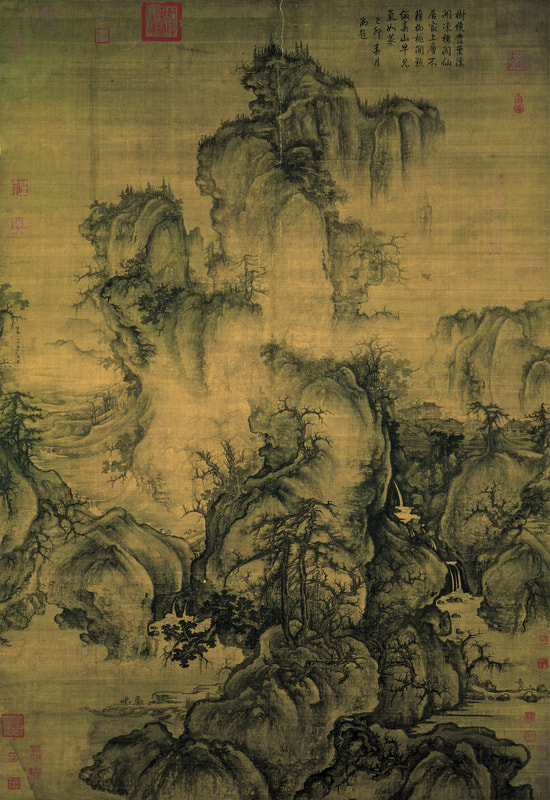
SHAN SHUI - CHINESE LANDSCAPE PAINTING
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 400 - 1700 DEFINING FEATURES:
|
|
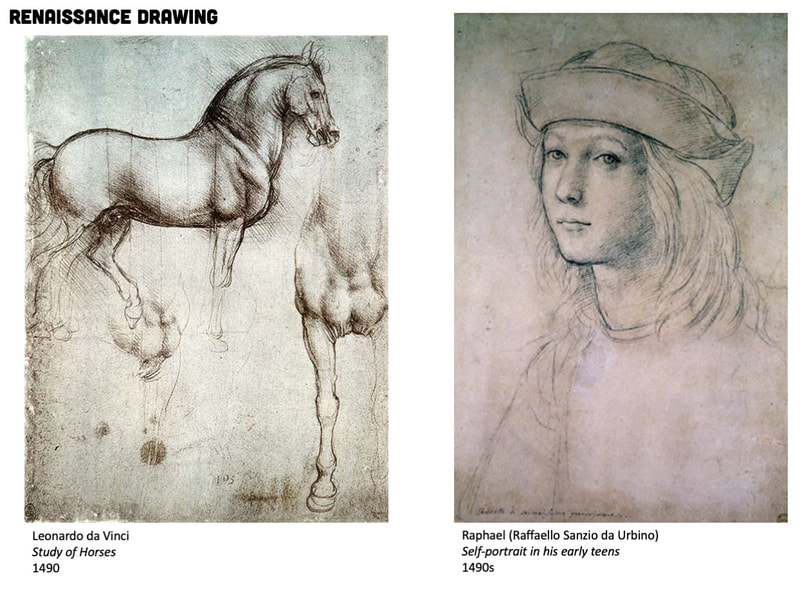
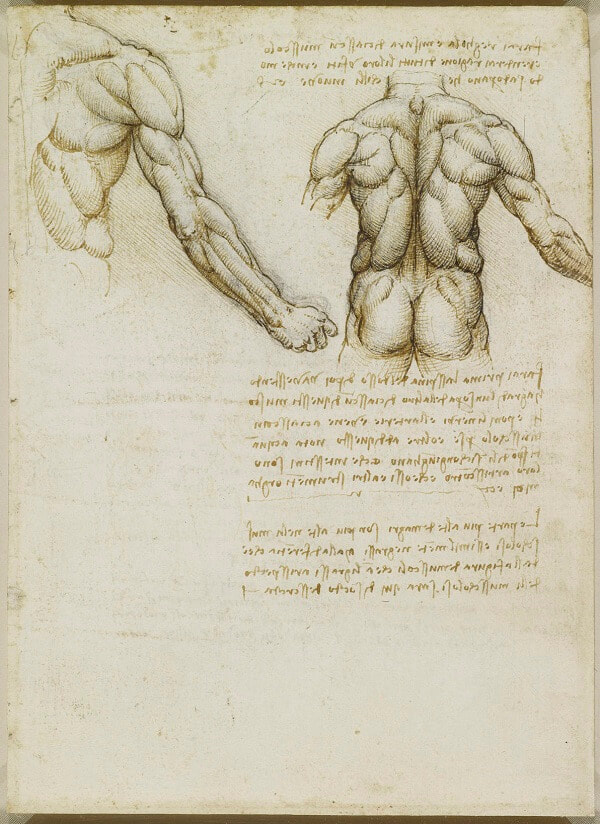
RENAISSANCE DRAWING
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 1400 - 1600 EUROPE DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Medici's Patronage of Art Renaissance VIDEO: Exploring the Renaissance for kids |
|
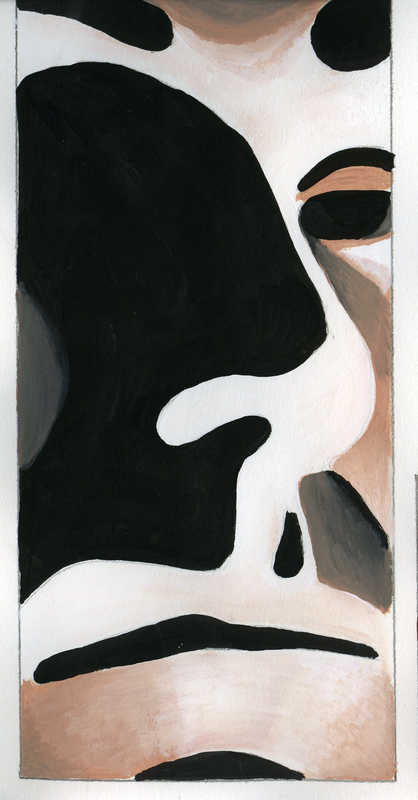
CHIAROSCURO & TENEBRISM
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 1600 EUROPE DEFINING FEATURES:
|
|
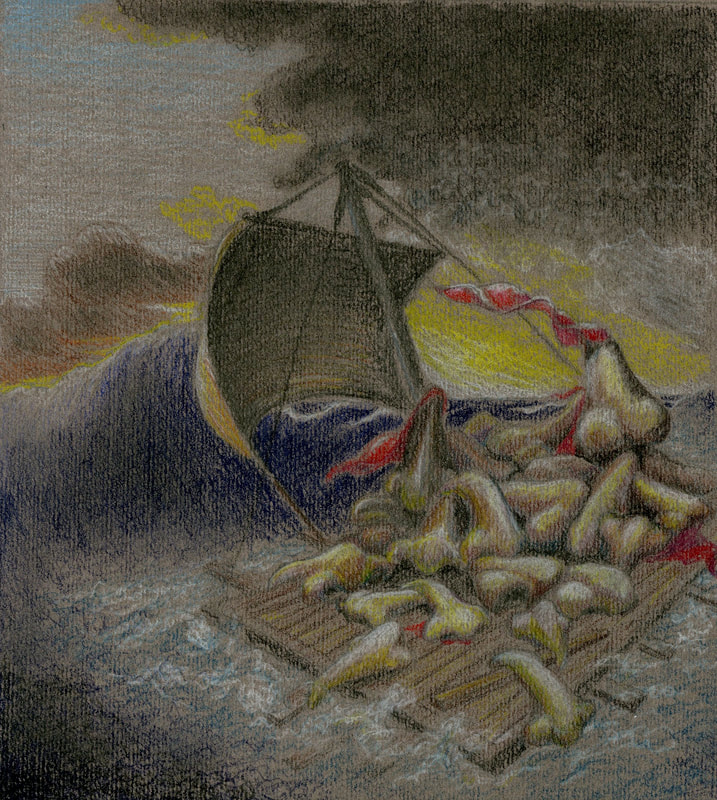
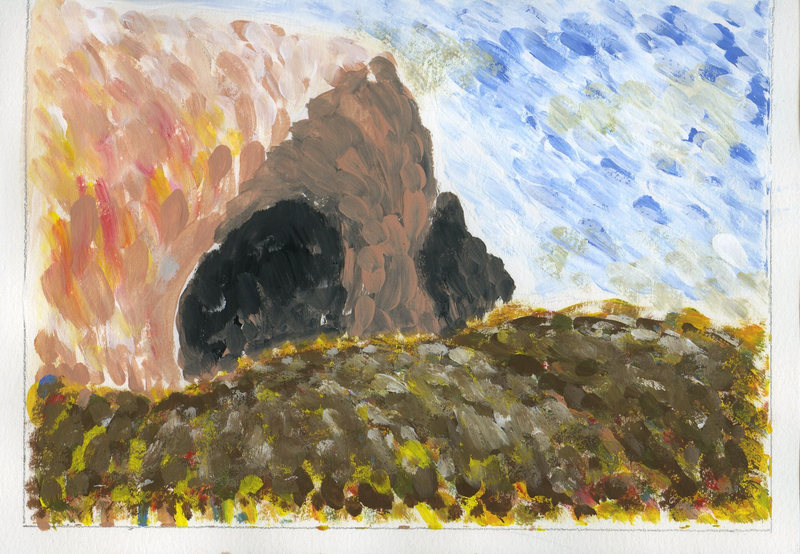
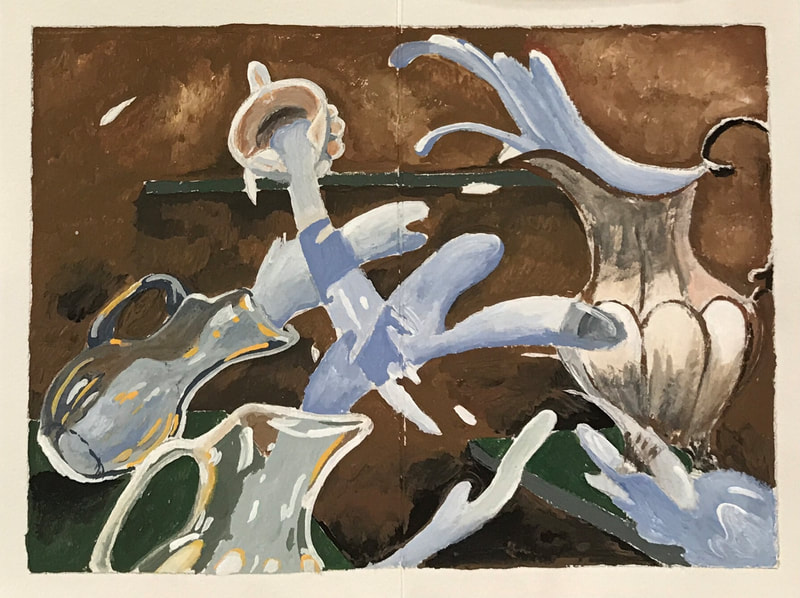
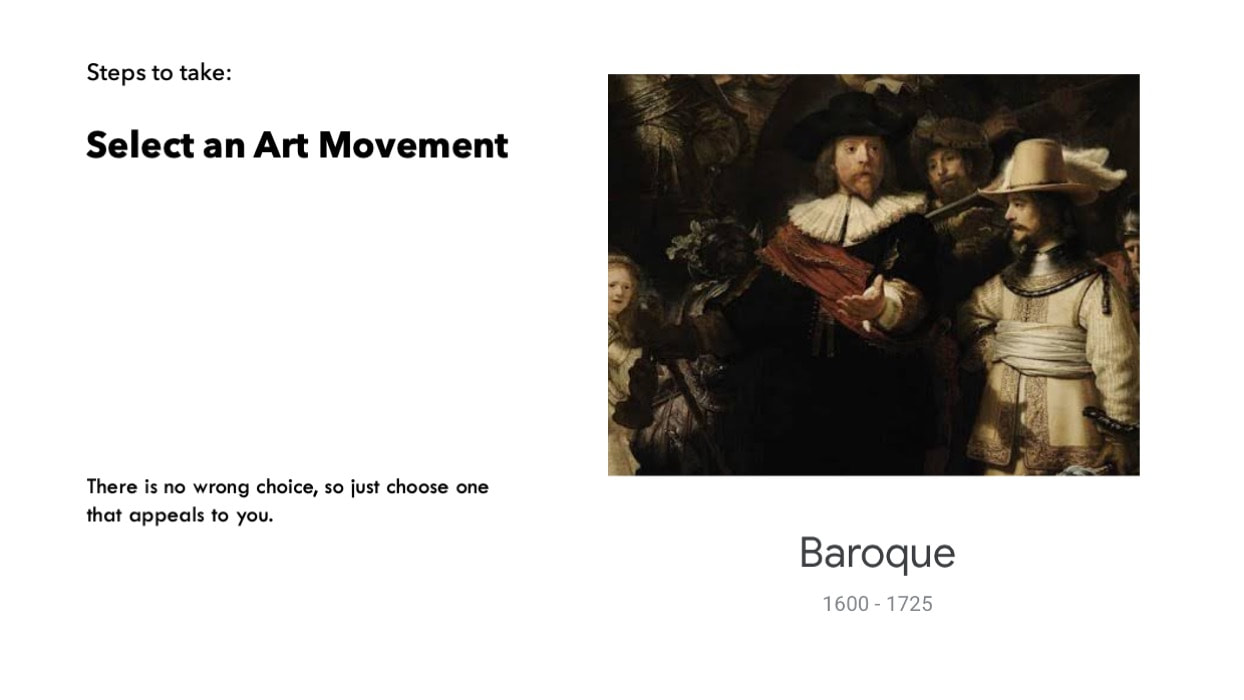
BAROQUE
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 1600 EUROPE DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Understanding Art Styles: Baroque |
|
UKIYO-E
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 1600 - 1900 Japan DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Ukiyo-e Explained |
|
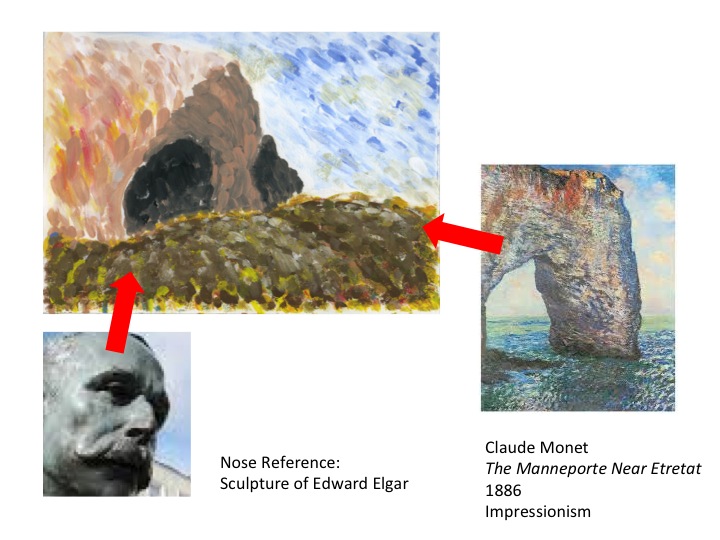
IMPRESSIONISM
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION : 1870 - 1900 France DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO : What is Impressionism? VIDEO : Monet painting water lilies (silent film) VIDEO : 10 Facts about Monet |
|
EXPRESSIONISM
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION : 1905 - 1930 Europe DEFINING FEATURES:
|
|
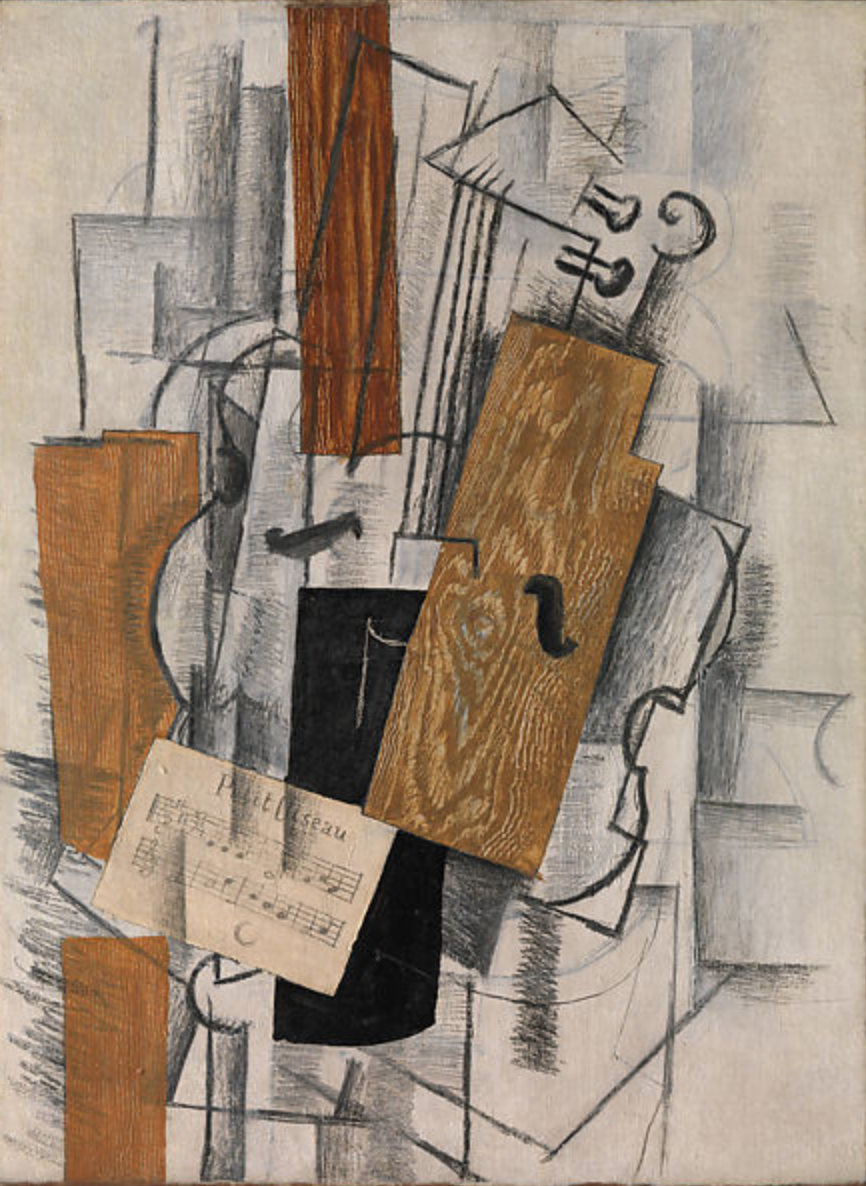
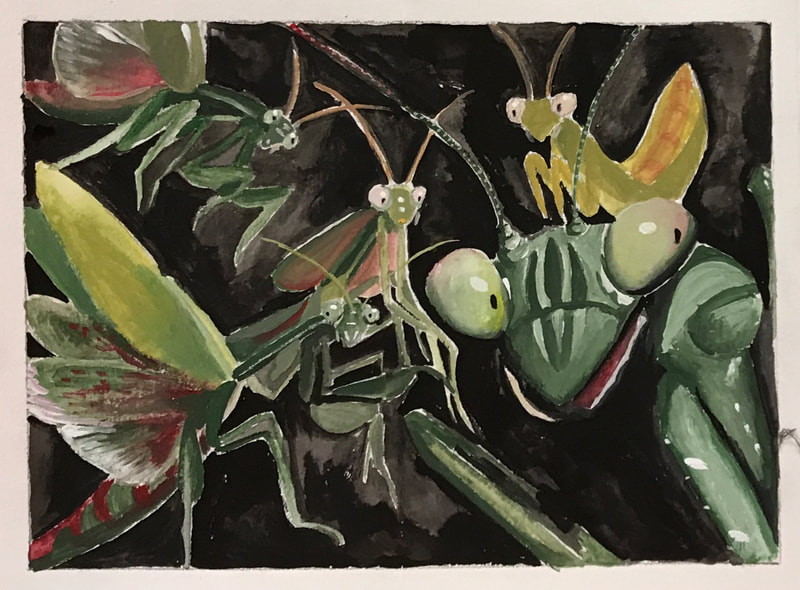
CUBISM
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION : 1910 - 1930 PARIS DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO : Why You Can't Be an Abstract Expressionist |
|
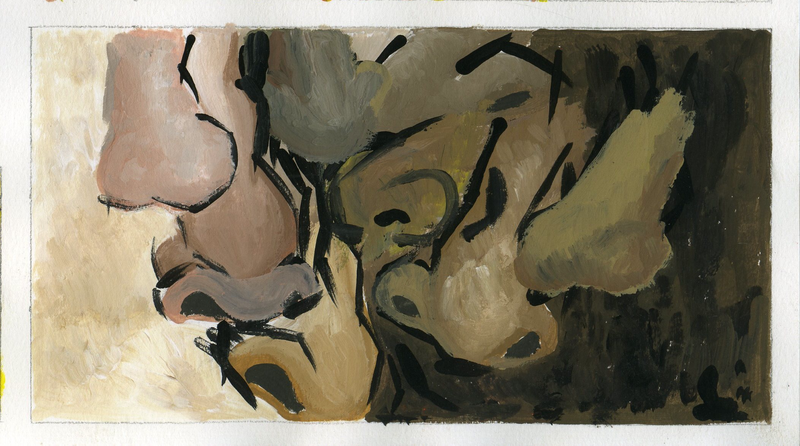
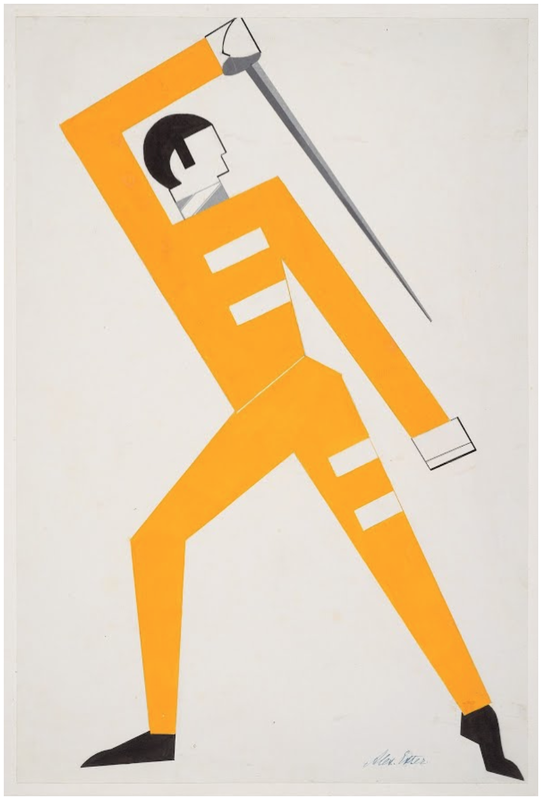
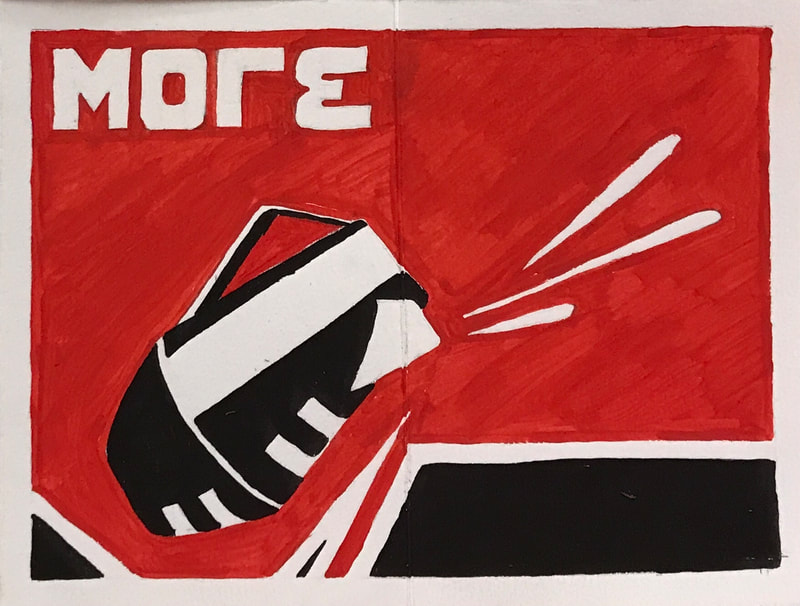
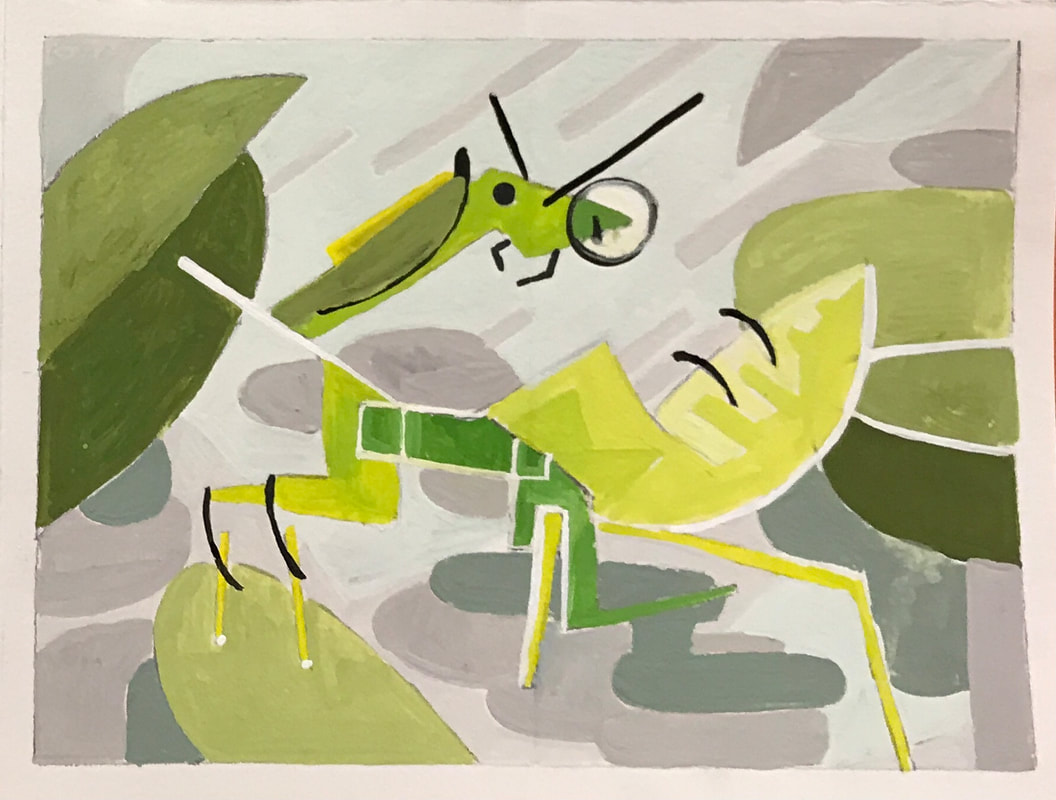
CONSTRUCTIVISM
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 1919 - 1932 Russia, then Europe DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Alexander Rodchenko |
|
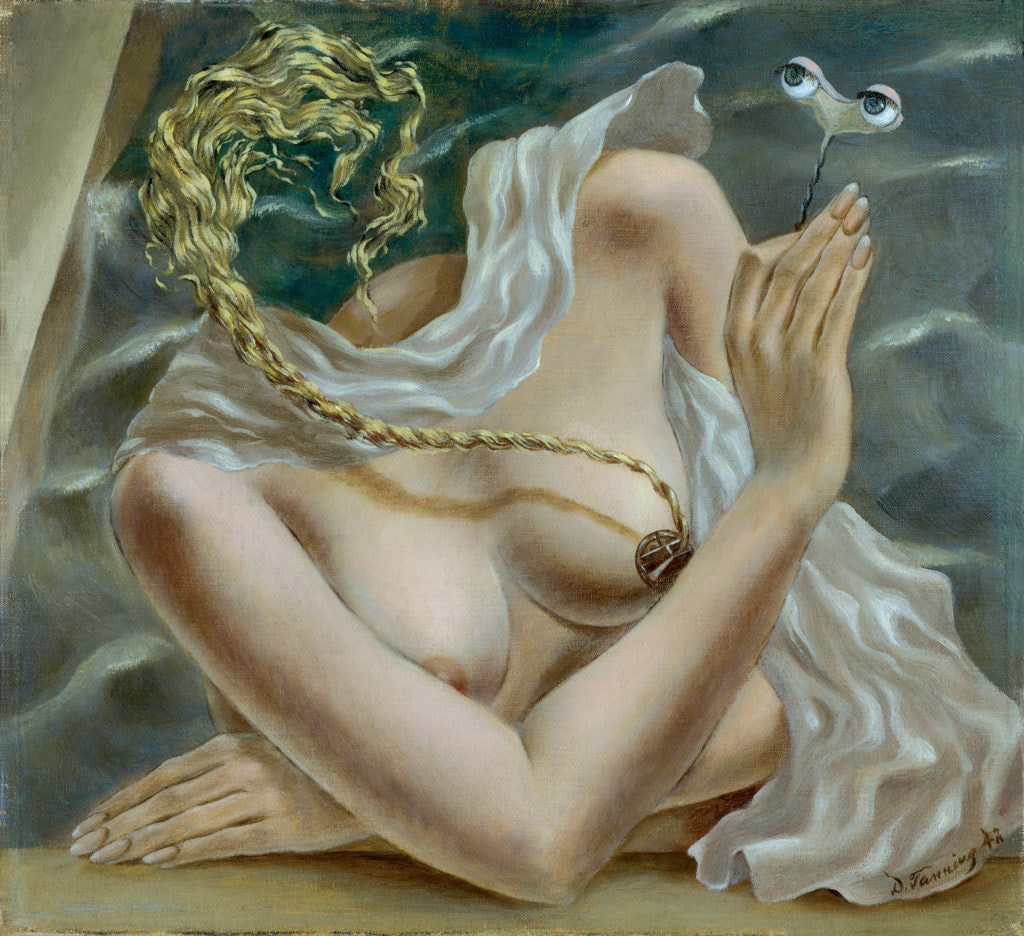
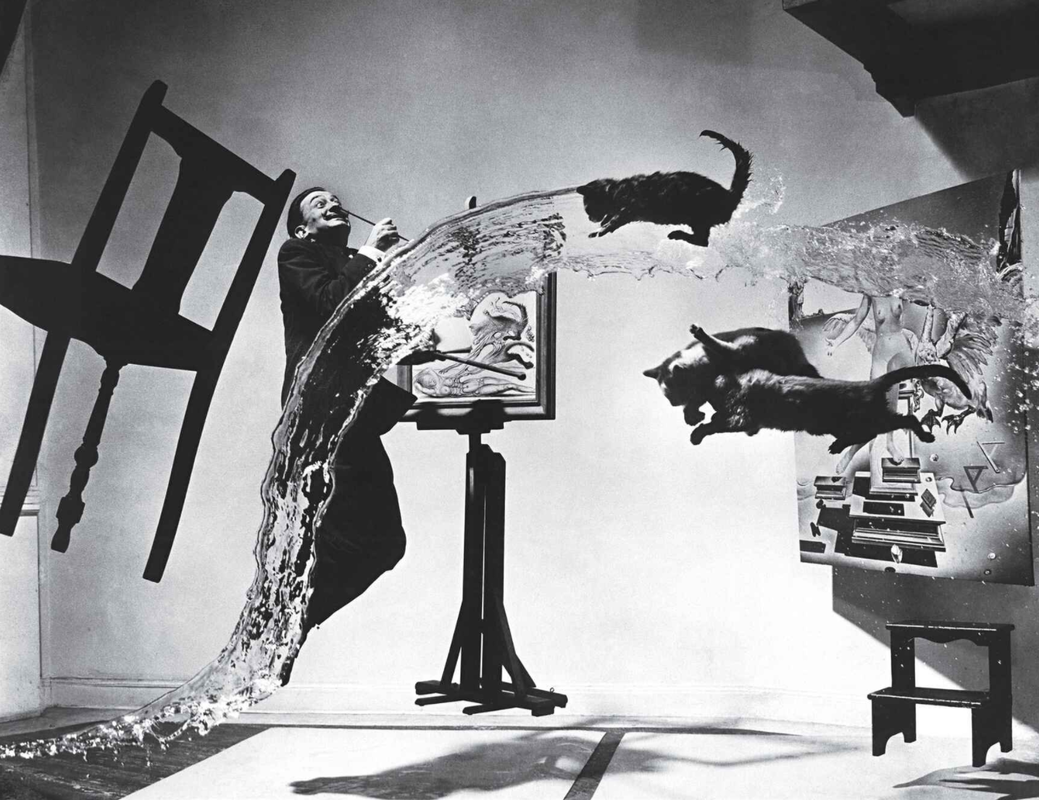
SURREALISM
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION : 1920 - 1950 France, Belgium DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO : Surrealism: The Big Idea |
|
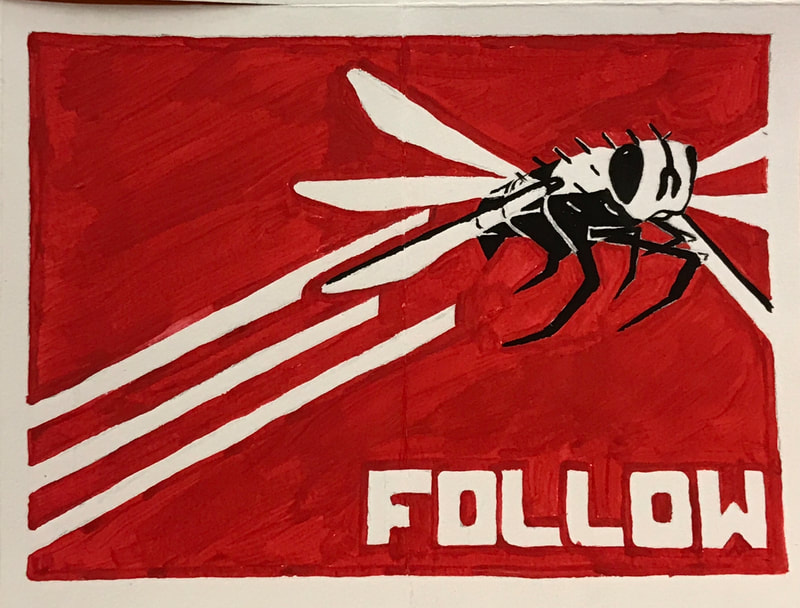
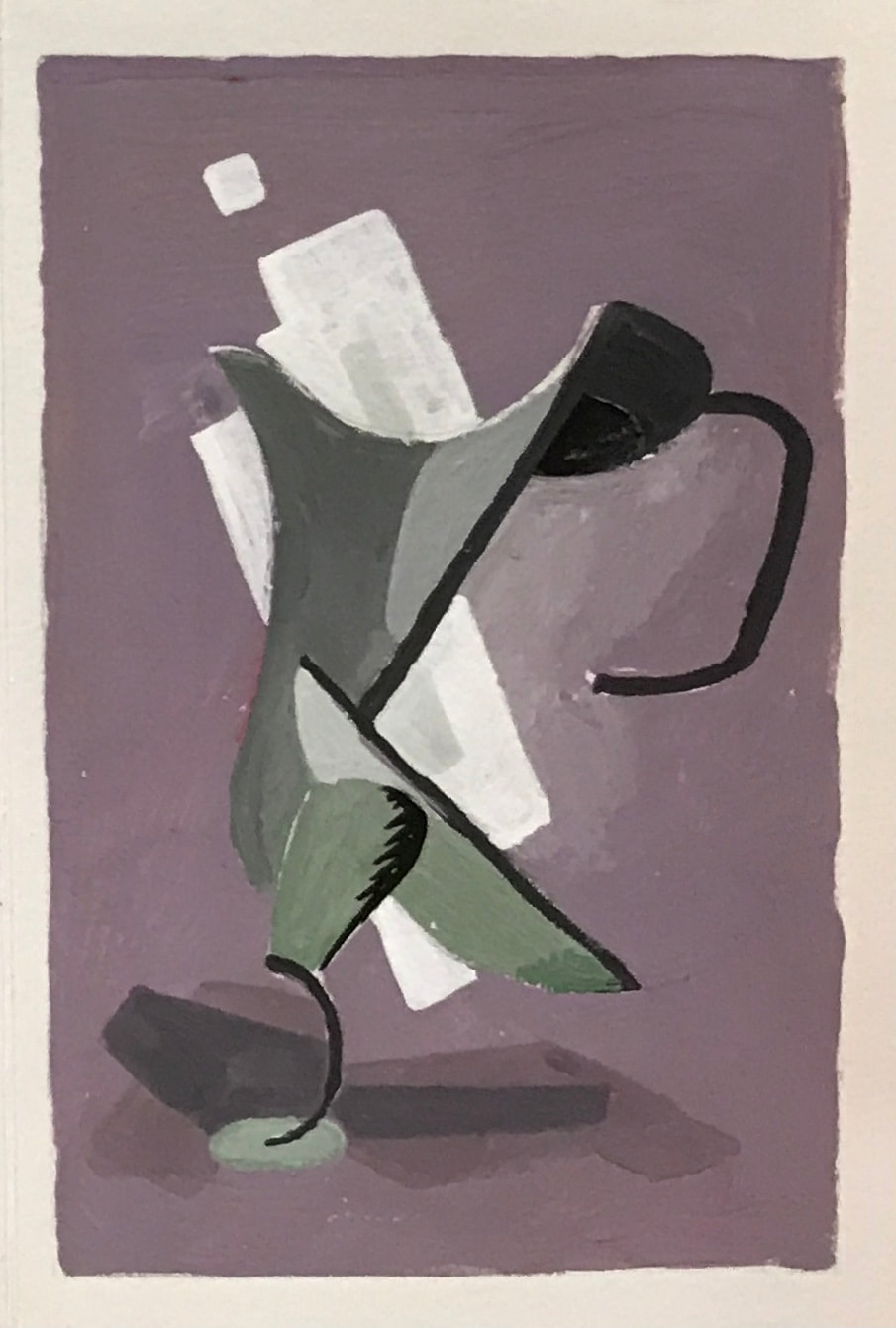
DADAISM
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION : 1915 - 1925 Zürich and Paris DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO : Sophie Tauber-Arp |
|
COLORFIELD PAINTING
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 1940 - 1960 New York DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Color Field Exhibit VIDEO: Mark Rothko VIDEO: Helen Frankenthaler / Frankenthaler 2 |
|
POP ART
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 1950 - 1960 US DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Roy Lichetenstein VIDEO: Andy Warhol |
|
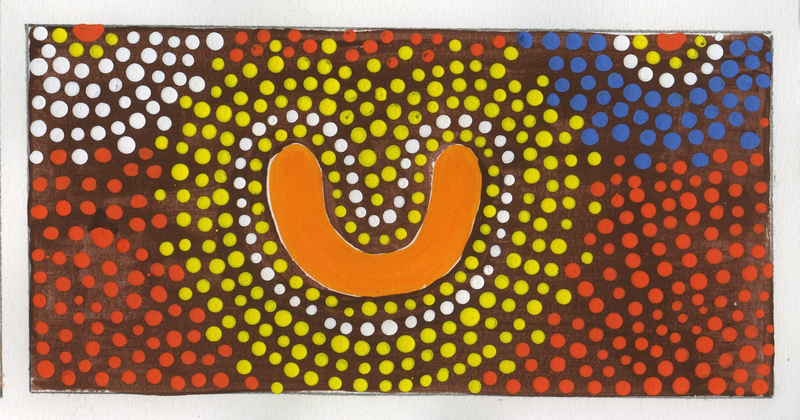
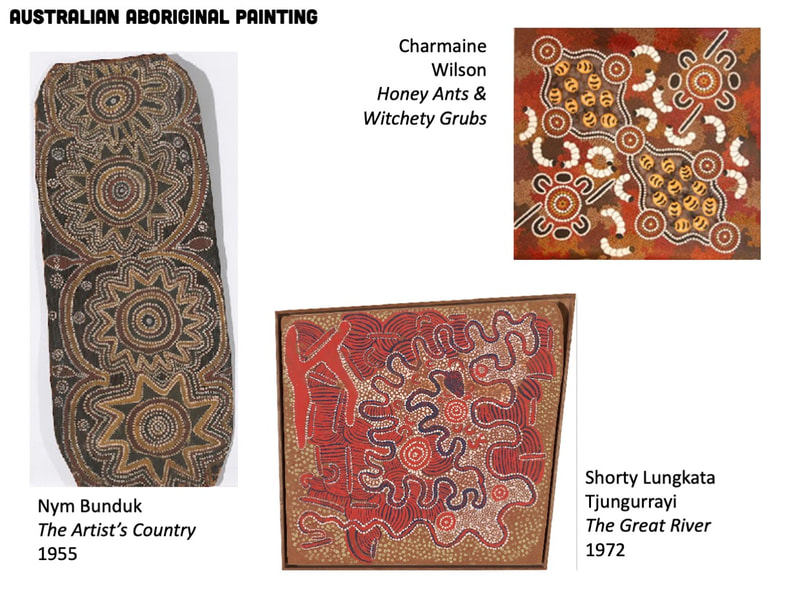
ABORIGINAL DOT PAINTING
TIME PERIOD & LOCATION: 1950 - Present Central Australia DEFINING FEATURES:
VIDEO: Aunty Ester Quinlin |
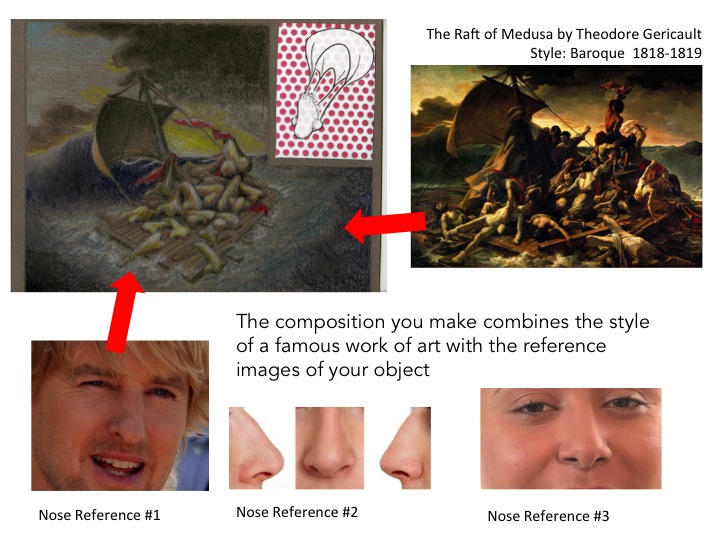
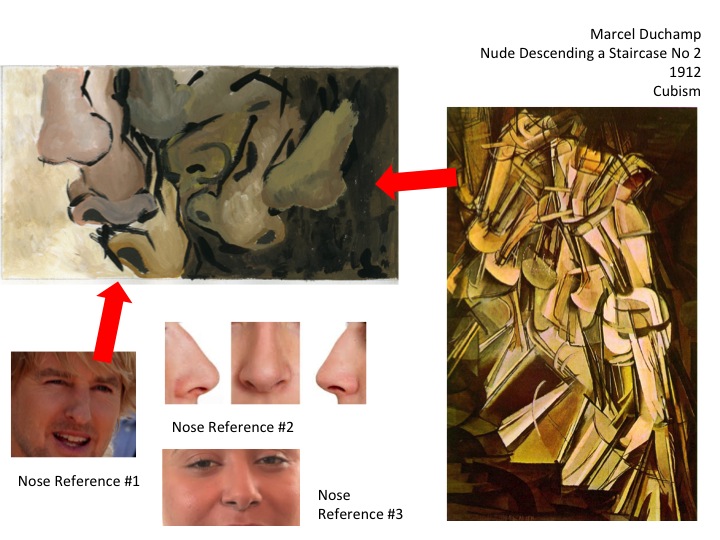
Using References to Create your Compositions
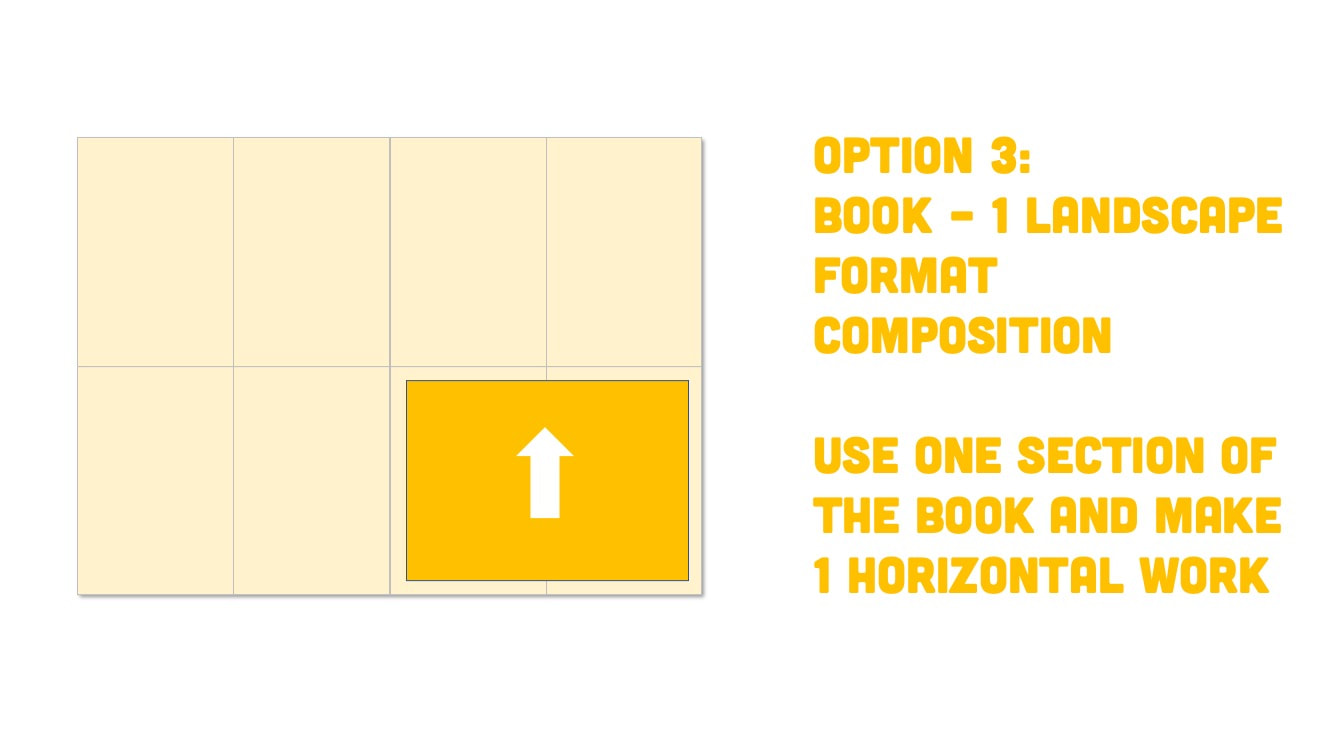
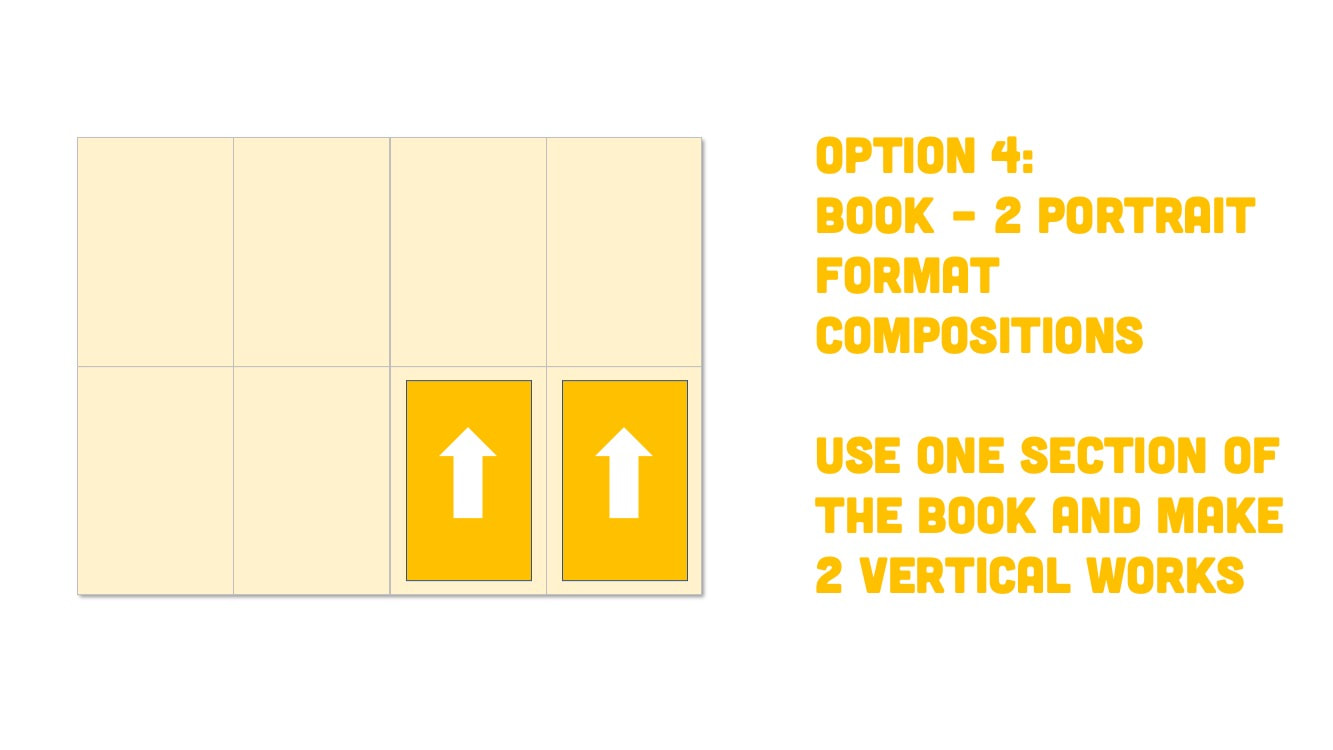
Paper Format Options
Examples
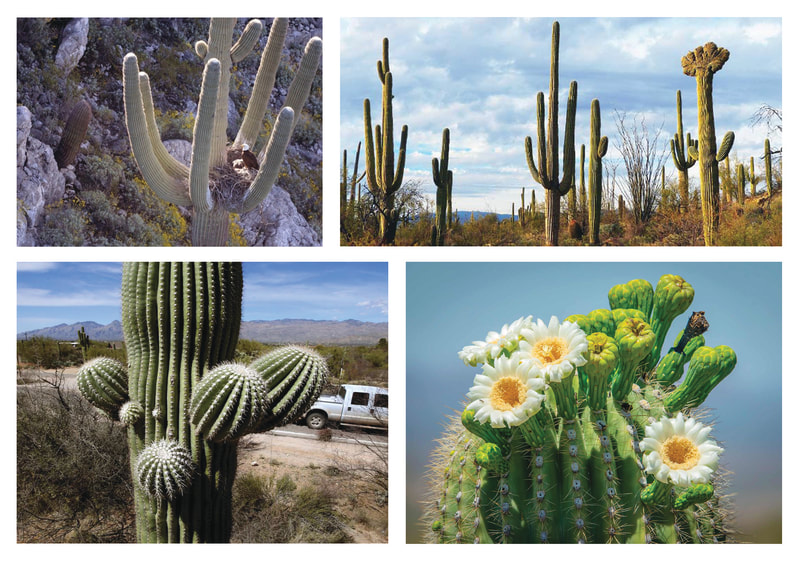
ART OBJECT
|
PITCHER
|
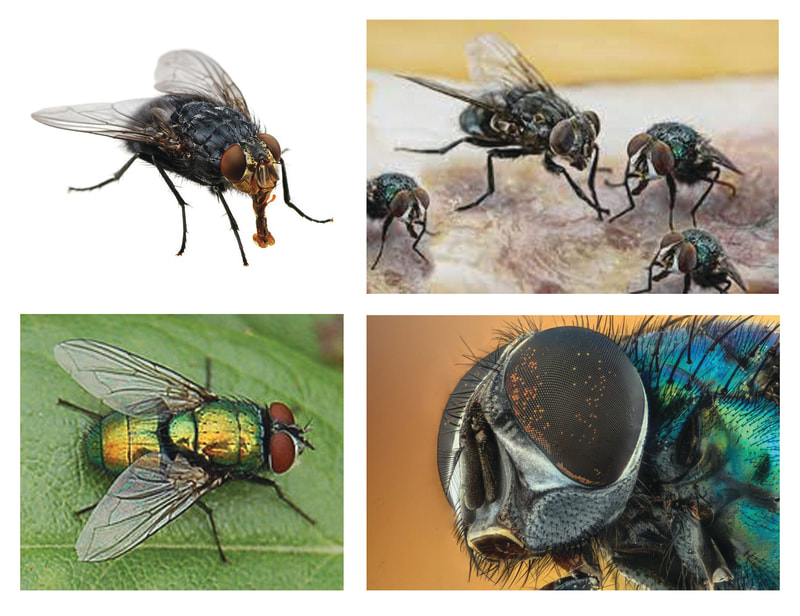
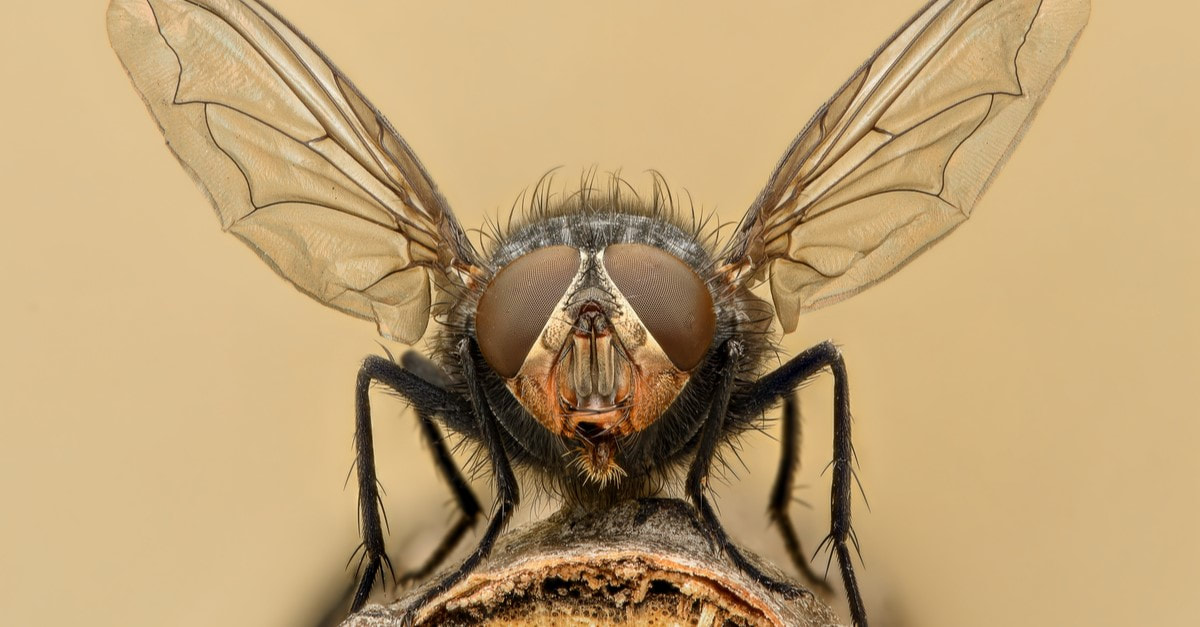
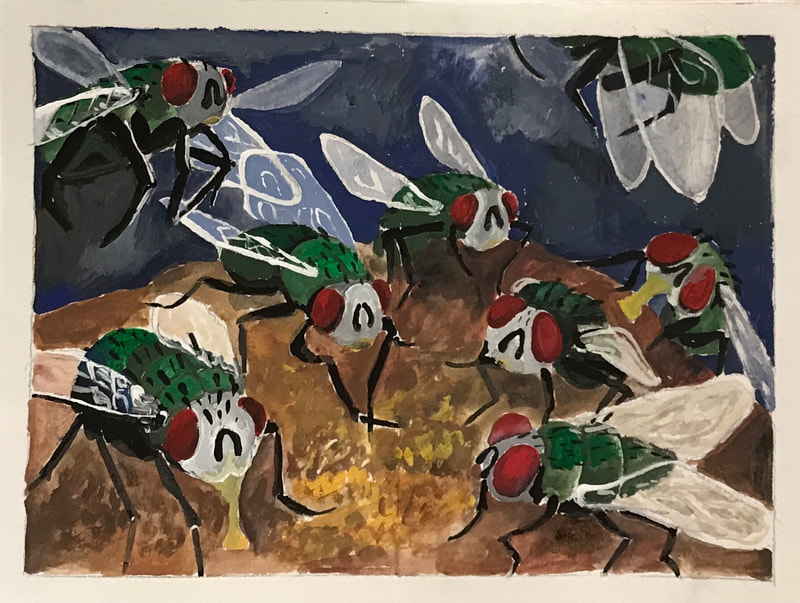
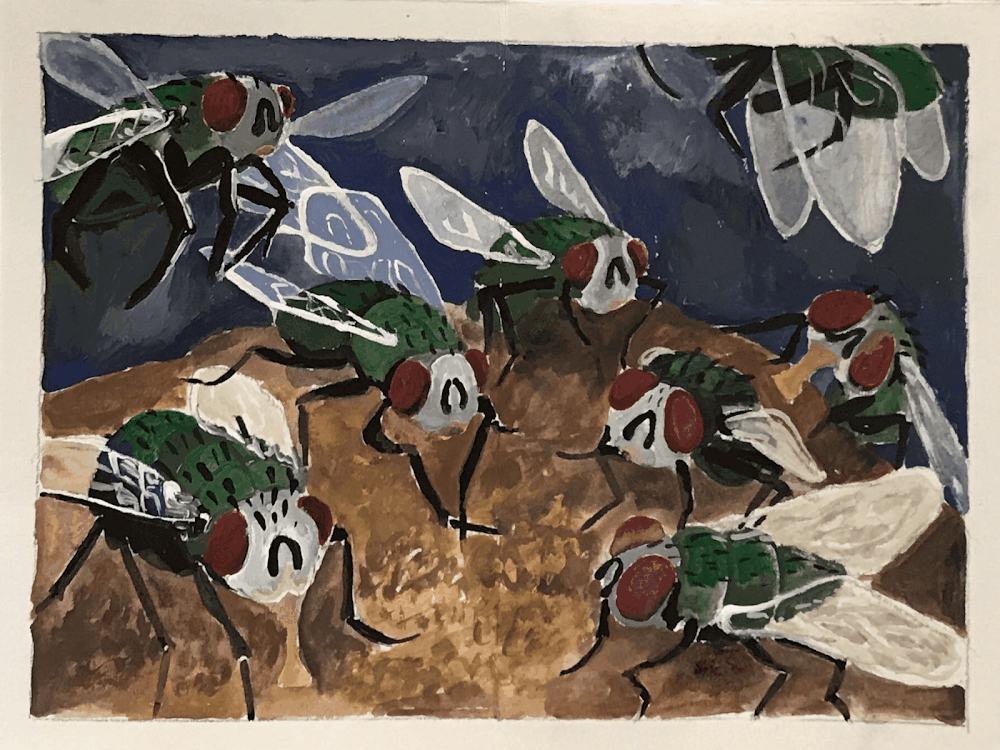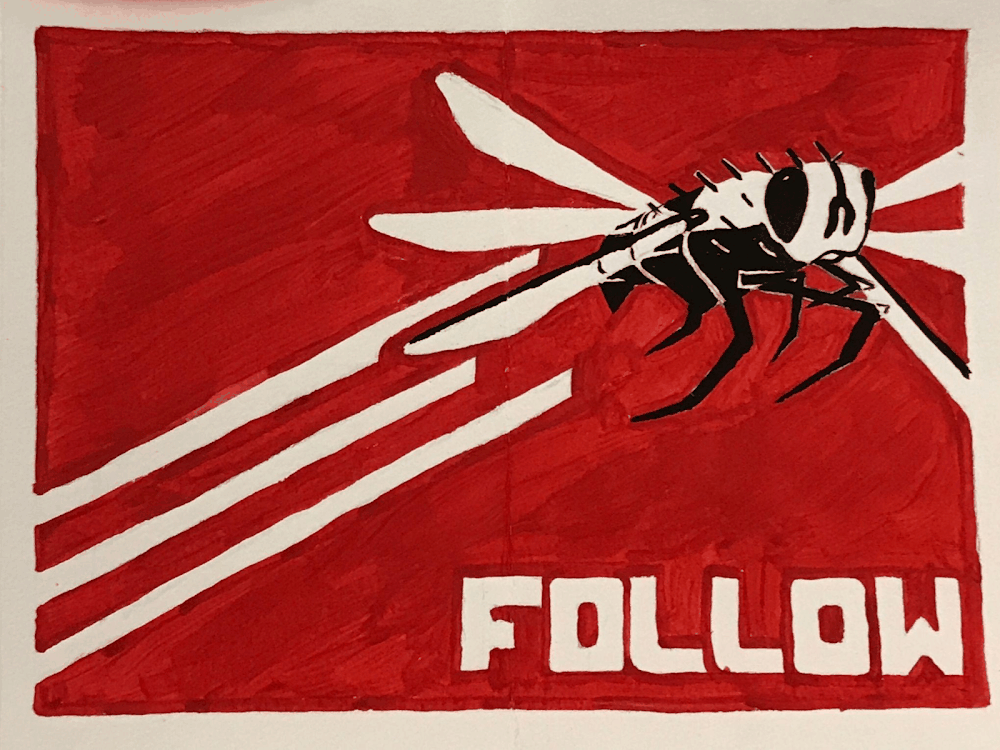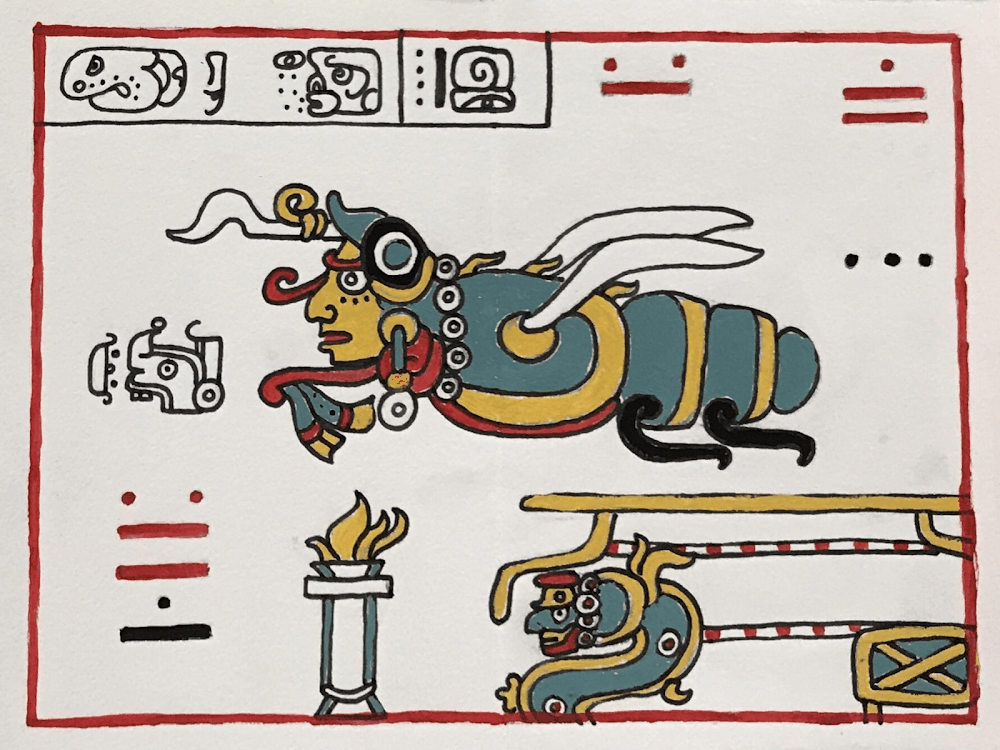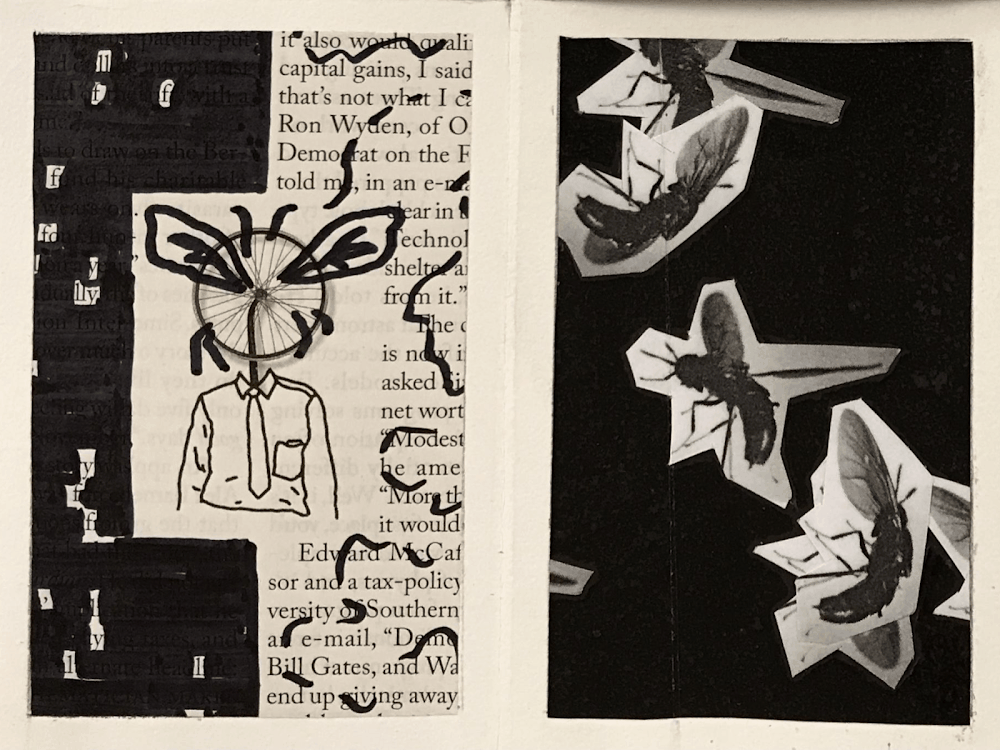
FLY
|
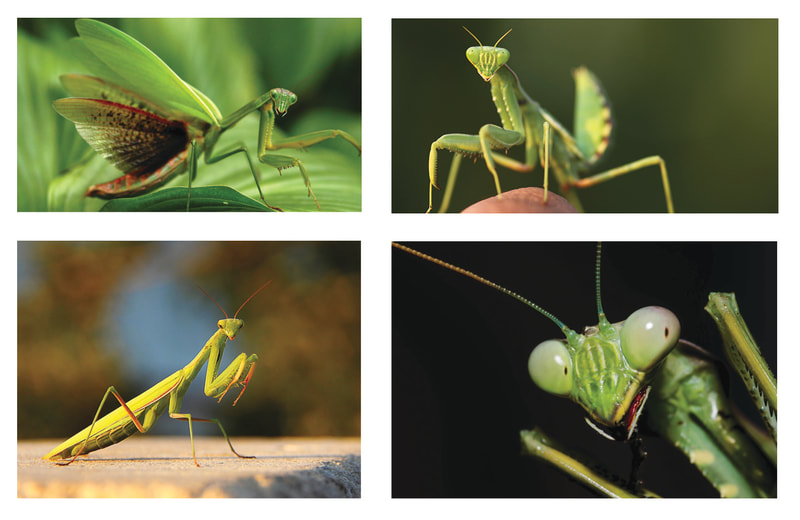
PRAYING MANTIS
|
ART STYLE : CONSTRUCTIVISM
ART STYLE : BAROQUE
ART STYLE : DADAISM
Video Instructions
|
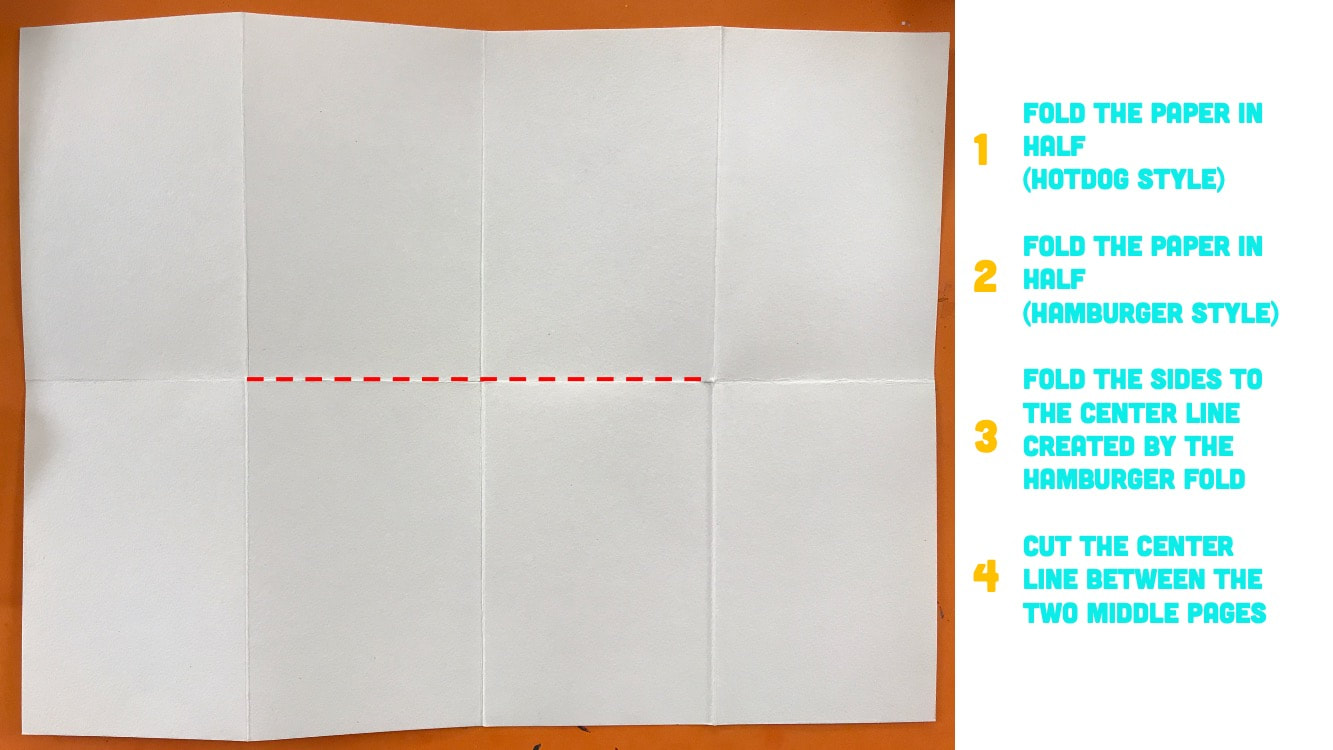
Optional Book Format |
Looping GIF of Collection of Things
|